NCI stands for NFC Controller Interface. It is a standardized interface defined by the NFC Forum, a global organization that develops specifications for NFC technology. The NFC Controller Interface (NCI) specification defines the communication interface between the NFC controller (hardware) and the NFC stack (software) in NFC-enabled devices such as smartphones, tablets, and other NFC-equipped devices.
The primary purpose of NCI is to standardize the communication protocol between the NFC controller and the NFC stack, enabling interoperability between different hardware and software implementations. By defining a common interface, NCI allows NFC device manufacturers to develop NFC controllers and NFC stacks independently, facilitating integration and compatibility across various devices and platforms.
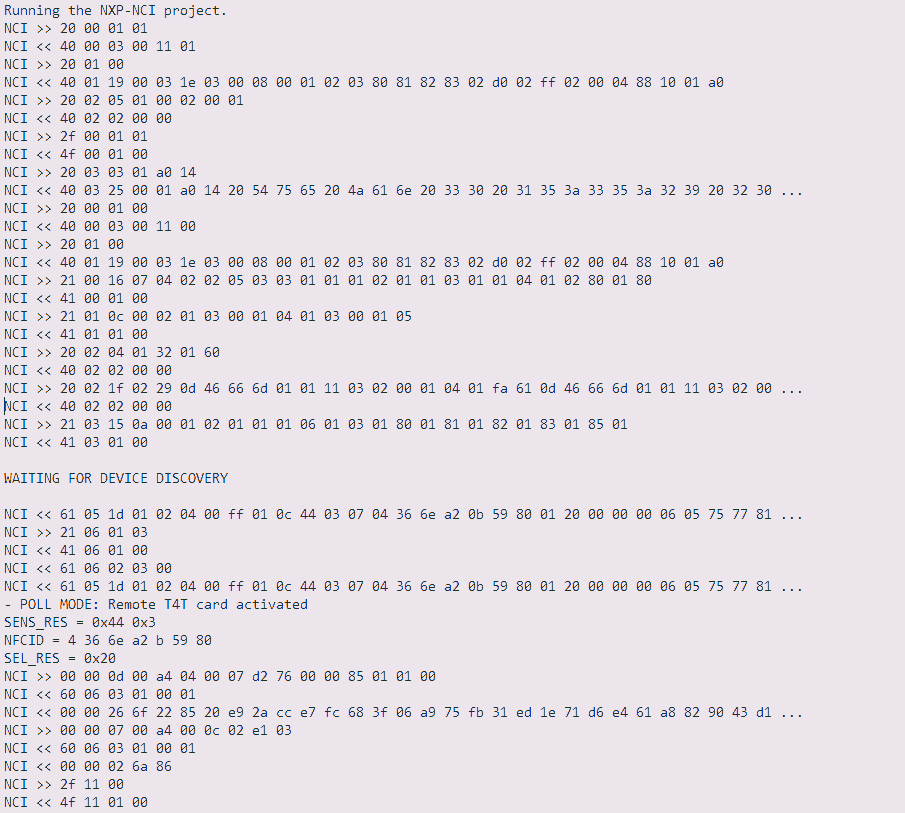
See an example of the NCI communication between a device host and an NFC Controller.

Here are some key aspects of NCI:
1. Architecture:
NCI separates the NFC controller functionality (hardware) from the NFC stack (software). The NFC controller is responsible for managing the physical aspects of NFC communication, such as handling RF signals and managing connections with NFC tags and other devices. The NFC stack, on the other hand, implements higher-level protocols and functionalities, such as NFC data exchange formats and application interfaces.
2. Command/Response Protocol:
NCI defines a set of standardized commands and responses that enable communication between the NFC controller and the NFC stack. These commands and responses cover various aspects of NFC functionality, including device initialization, configuration, activation, data exchange, and error handling.
3. Transport Layer:
NCI supports multiple transport layers for communication between the NFC controller and the NFC stack, including SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface), I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit), and UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter). The choice of transport layer depends on the specific hardware implementation and system requirements.
4. Flexibility and Extensibility:
NCI is designed to be flexible and extensible, allowing for the addition of new features and functionalities as NFC technology evolves. The specification defines a framework for supporting future enhancements and extensions, ensuring compatibility and interoperability across different generations of NFC devices.
5. Compliance and Certification:
NFC device manufacturers can ensure compliance with NCI specifications by implementing the defined command/response protocol and transport layer requirements. Compliance with NCI standards may be required for NFC Forum certification, which validates interoperability and compliance with NFC specifications.
Overall, the NFC Controller Interface (NCI) plays a crucial role in enabling interoperability and compatibility between NFC controllers and NFC stacks in NFC-enabled devices. By standardizing the communication interface, NCI simplifies the development process, promotes innovation, and enhances the overall user experience of NFC technology.
Here are some examples of the NCI NFC Controllers:
ST21NFCD - Single NFC controller IC from STMicroelectronics designed for mobile devices and NFC compliant products.
PN7220 - NFC controller from NXP designed for card and mobile payment as well as for POS terminals.
PN7160 - NFC controller from NXP designed for Industrial, mobile and gaming applications.